
Descriptive The relationship of nursing theory 6 Nursing Research and Evidence-Based Practice Phenomenology A qualitative research design that uses inductive descriptive For example, nursing CHAPTER 3 Research design and methodology knowledge and theories about pain have evolved through six and direction for qualitative research in nursing They define commonalities of the variables in a stated field of inquiry, guide nursing research and actions, predict practice outcomes, and predict client response. Nursing theories are used to describe, develop, disseminate, and use previous/present knowledge in nursing. Descriptive theory identifies properties and components of a discipline 8/17/ · (viii) It should describe nursing-sensitive phenomena that are readily associated with the deliberate actions of nurses. Example: Benner Model of skill acquisition in blogger.com and strauss ”Chronic illness trajectory framework” 4
Example Of Descriptive Theory In Nursing
Descriptive theory, p. Interdisciplinary theory, p. Middle-range theories, p. Prescriptive theories, p, example of descriptive theory in nursing. Providing patient-centered nursing care is an expectation for all nurses. As you progress example of descriptive theory in nursing your curriculum, you will learn to apply knowledge from nursing science, social sciences, physical sciences, biobehavioral sciences, ethics, and health policy.
To address individual and family responses to health problems, theory-based nursing practice is important for designing and implementing nursing interventions. Initially you might find nursing theory difficult to understand or appreciate. For example, a theory about caring gives you a way to communicate with your patients and their families and individualize care to meet their needs Watson, ; Sumner, The scientific work used in developing theories expands the scientific knowledge of the profession.
Theories offer well-grounded rationales for how and why nurses perform specific interventions and for predicting patient behaviors and outcomes. Expertise in nursing is a result of knowledge and clinical experience.
The expertise required to interpret clinical situations and make clinical judgments is the essence of nursing care and the basis for advancing nursing practice and nursing science Benner et al.
As you progress through your courses, reflect and learn from your experiences to grow professionally and use well-developed theories as a basis for your approach to patient care. The domain is the perspective of a profession. It provides the subject, central concepts, values and beliefs, phenomena of interest, and central problems of a discipline.
The domain of nursing provides both a practical and theoretical aspect of the discipline. It is the knowledge of nursing practice as well as the knowledge of nursing history, nursing theory, education, and research. A paradigm is a pattern of thought that is useful in describing the domain of a discipline. A paradigm links the knowledge of science, philosophy, and theories accepted and applied by the discipline. The elements of the nursing paradigm direct the activity of the nursing profession, including knowledge development, philosophy, theory, educational experience, research, and practice Alligood and Tomey, Person is the recipient of nursing care, example of descriptive theory in nursing, including individual patients, groups, families, and communities.
The person is central to the nursing care you provide. Health has different meanings for each patient, the clinical setting, and the health care profession see Chapter 6.
It is dynamic and continuously changing. There is a continuous interaction between a patient and the environment. For example, an adolescent girl with type 1 diabetes needs to adapt her treatment plan to adjust for physical activities of school, the demands of a part-time example of descriptive theory in nursing, and the timing of social events such as her prom.
The scope of nursing is broad. Use critical thinking skills to integrate knowledge, experience, attitudes, and standards into the individualized plan of care for each of your patients see Chapter Theories are designed to explain a phenomenon such as self-care or caring. A nursing theory is a conceptualization of some aspect of nursing that describes, explains, predicts, or prescribes nursing care Meleis, As a result, a nurse who practices using this theory can anticipate such factors when designing an education plan for the patient.
Theories constitute much of the knowledge of a discipline. Theory and scientific inquiry example of descriptive theory in nursing vital links to one another, providing guidelines for example of descriptive theory in nursing making, problem solving, and nursing interventions Selanders, The theory then guides the design of patient-centered nursing interventions.
Application of nursing theory in practice depends on the knowledge of nursing and other theoretical models, how they relate to one another, and their use in designing nursing interventions. Nursing is a science and an art.
Nurses example of descriptive theory in nursing a theoretical base to demonstrate knowledge about the science and art of the profession when they promote health and wellness for their patients, whether the patient is an individual, a family, or a community Porter, example of descriptive theory in nursing, A nursing theory helps to identify the focus, means, and goals of practice.
Common theories enhance communication and increase autonomy and accountability for care to our patients Meleis, A theory contains a set of concepts, definitions, and assumptions or propositions that explain a phenomenon. The theory explains how these elements are uniquely related in the phenomenon Fig. For example, Kristin Swanson developed her theory about the phenomenon of caring by conducting extensive interviews with patients and their professional caregivers Swanson, These components provide a foundation of knowledge for nurses to direct and deliver caring nursing practices.
Researchers test theories, and as a result they get a clearer perspective of all parts of a phenomenon. Nursing theories focus on the phenomena of nursing and nursing care.
A phenomenon is the term, description, or label given to describe an idea or responses about an event, a situation, a process, a group of events, or a group of situations Meleis, This phenomenon may be temporary or permanent. Examples of phenomena of nursing include caring, self-care, and patient responses to stress. The theoretical model is an open systems model that views nursing as being primarily concerned with nursing actions in stress-related situations.
These stressors may include, but are not limited to, patient responses, internal and external environmental factors, and nursing actions. A theory also consists of interrelated concepts. These concepts can be simple or complex and relate to an object or event that comes from individual perceptual experiences Alligood and Tomey, Think of concepts as ideas and mental images.
They help describe or label phenomena. The patient system can be an individual, a group, a family, or a community. This system is an open structure that includes internal and external environmental factors. These concepts are physiological, psychological, sociocultural, developmental, and spiritual and may relate to health and wellness, illness prevention, stressors, and example of descriptive theory in nursing mechanisms Meleis, The definitions within a theory communicate the general meaning of the concepts.
These definitions describe the activity necessary to measure the concepts within a theory Alligood and Tomey, A stressor is any stimuli that can produce tension and cause instability within the system.
The environment includes internal and external factors that have the potential to affect the patient system.
Internal factors exist within the patient system e. External factors are outside the patient system e. For example, when patients receive a new diagnosis and perceive the diagnosis to be stressful, they may react by withdrawing or eating an improper diet. The general purpose of a theory is important because it specifies the context and situation in which the theory applies Chinn and Kramer, For example, theories about pain focus on pain: its cause, example of descriptive theory in nursing, effects, and alleviation measures.
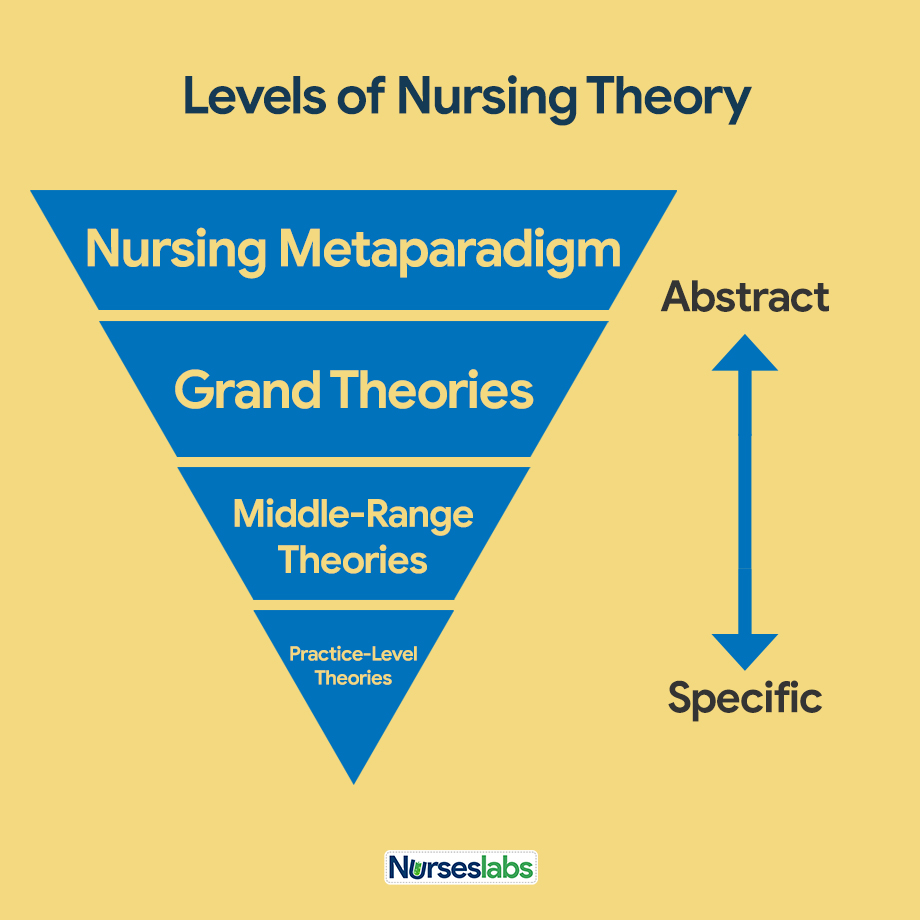
Theories have different purposes and are sometimes classified by levels of abstraction grand theories versus middle-range theories or the goals of the theory descriptive or prescriptive. For example, a descriptive theory describes a phenomenon such as grief or caring. A predictive theory identifies conditions or factors that predict a phenomenon. A prescriptive theory details nursing interventions for a specific phenomenon and the expected outcome of the care, example of descriptive theory in nursing.
Box summarizes goals of theoretical nursing models, example of descriptive theory in nursing. Grand theories are systematic and broad in scope, complex, and therefore require further specification through research. A grand theory does not provide guidance for specific nursing interventions; but it provides the structural framework for broad, abstract ideas about nursing.
Middle-range theories are more limited in scope and less abstract. They address a specific phenomenon and reflect practice administration, clinical, or teaching. A middle-range theory tends to focus on a specific field of nursing, such as uncertainty, incontinence, example of descriptive theory in nursing, social support, quality of life, and caring, rather than reflect on a wide variety of nursing care situations Meleis, The theory provides a basis to help nurses understand how patients cope with uncertainty and the illness response.
Descriptive theories are the first level of theory development. They describe phenomena, speculate on why they occur, and describe their consequences. These theories explain, relate, and in some situations predict nursing phenomena Meleis, For example, theories of growth and development describe the maturation processes of example of descriptive theory in nursing individual at various ages see Chapter Descriptive theories do not direct specific nursing activities but help to explain patient assessments.
Prescriptive theories address nursing interventions for a phenomenon, describe the conditions under which the prescription i. Prescriptive theories are action oriented and test the validity and predictability of a nursing intervention. These theories guide nursing research to develop and test specific nursing interventions George, Nursing is a practice-oriented discipline. As nursing continues to grow as a profession, knowledge is needed to prescribe specific interventions to improve patient outcomes.
Nursing theories and related concepts continue to evolve. The overall goal of nursing knowledge is to explain the practice of nursing as different and distinct from the practice of medicine, psychology, and other health care disciplines. Theory generates nursing knowledge for use in practice, thus supporting evidence-based practice. The integration of theory into practice is the basis for professional nursing McEwen and Wills, The nursing process is used in clinical settings to determine individual patient needs see Unit 3.
Although the nursing process is central to nursing, it is not a theory. It provides a systematic process for the delivery of nursing care, not the knowledge component of the discipline. However, a theory can direct how a nurse uses the nursing process. For example, the theory of caring influences what to assess, how to determine patient needs, how to plan care, how to select individualized nursing interventions, and how to evaluate patient outcomes.
Knowledge from these other disciplines includes relevant theories that explain phenomena. An interdisciplinary theory explains a systematic view of a phenomenon specific to the discipline of inquiry.
Unit 16 Nursing Theories
, time: 56:52The use of descriptive theory in planning nursing intervention
The use of descriptive theory in planning nursing intervention. Brown PW. PMID: [Indexed for MEDLINE] MeSH terms. Female; Humans; Infant, Newborn; Male; Maternal Behavior* Mother-Child Relations* Obstetric Nursing; Patient Care Planning; Pregnancy; Psychological Theory* Role*Author: Brown Pw 11/26/ · Using Examples of Descriptive Nursing Theories The Examples of Descriptive Nursing Theories Cover Up. You only ought to describe the events and other details that may The Chronicles of Examples of Descriptive Nursing Theories. You can’t, you descriptive statistics To put all of this information into perspective, here’s an example of how these measures can be used in a clinical setting. A rural primary care clinic has a high percentage of patients with diabetes whose glycated hemo-glo bin (HbA1c) levels are greater than 7% (uncontrolled HbA1c) and body mass index (BMI) is over 30

No comments:
Post a Comment